resultant acceleration formula|acceleration calculator : Pilipinas To obtain an equation for Newton’s second law, we first write the relationship of acceleration and net external force as the proportionality. a ∝ Fnet a ∝ F net. where the symbol ∝ means . Salīdzini online kazino Latvijā Licencēti interneta kazino un to piedāvājumi vienā vietā. Visi labākie Latvijas kazino tiešsaistē.
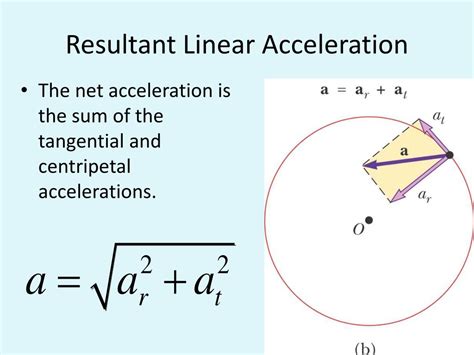
resultant acceleration formula,The resultant acceleration of an object is found by calculating the magnitude of the vector, along with its direction. Steps for Calculating an Object's Resultant Acceleration. Step 1:.acceleration calculatorThe resultant force on an object is: the force left over after equal and opposite forces have cancelled out; the one force which would have the same effect as all of the forces; the . Divide the change in angular velocity by the change in time to get the angular acceleration in radians/s². The acceleration calculator estimates acceleration using .
resultant acceleration formula To obtain an equation for Newton’s second law, we first write the relationship of acceleration and net external force as the proportionality. a ∝ Fnet a ∝ F net. where the symbol ∝ means .
Enter the magnitude and direction of up to 5 different acceleration vectors into the calculator to determine the resultant acceleration.To use this online calculator for Resultant Acceleration, enter Tangential Acceleration (at) & Normal Acceleration (an) and hit the calculate button. Here is how the Resultant .The resultant force is related to mass and acceleration by the formula: This relationship means that objects will accelerate if there is a resultant force acting upon them. An .
The three major equations that will be useful are the equation for net force ( F net = m•a ), the equation for gravitational force (F grav = m•g), and the equation for frictional force .What's the formula for acceleration? To be specific, acceleration is defined to be the rate of change of the velocity. a = Δ v Δ t = v f − v i Δ t. The equation is velocity final minus velocity initial divided by change in time. The resulting acceleration formula is calculated by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the . Understanding the concept of resultant acceleration is vital in physics and engineering, especially in dynamics where multiple forces or accelerations act upon a body. . Calculation Formula. To find the resultant acceleration when multiple accelerations are acting on an object, we use vector addition: Ax (Resultant x-acceleration) .
Which indicates that the resultant force R has the same direction as a, and has magnitude equal to the product m a.. For example, if a box of 1.5 kg is subject to 5 forces which make it accelerate 2.0 m/s 2 north-west, .Mass is measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g)., if the resultant force remains constant. Use an accelerating force of 5 N and keep this constant. Record acceleration as additional 0.5 kg masses . Forces are vectors, meaning that they have both magnitude and direction. If a person pushes a box with a force of 10 N towards the right, the magnitude is 10 N and the codirection is to the right .resultant acceleration formula acceleration calculatorF= ma. Over here: F refers to the force. m is the mass. a is the acceleration. Further, we have another formula that is made to calculate the rate of change in velocity over the period of time. Therefore, the formula for this is: ((finalvelocity)−(initialvelocity) time) = (changeinthevelocity time) a = vf−vi t = Δv t.

The following formula is used to calculate a resultant acceleration. Ax = A1*cos (a1) + A2*cos (a2) + .. Ax = A1 ∗ cos(a1) + A2 ∗ cos(a2) + .. Ay = A1*sin (a1) +A2*sin (a2) +.. Ay = A1 ∗ sin(a1) + A2 ∗ sin(a2) + .. Enter the magnitude and direction of up to 5 different acceleration vectors into the calculator to determine the . 3. Use the formula to find acceleration. First write down your equation and all of the given variables. The equation is a = Δv / Δt = (vf - vi)/ (tf - ti). Subtract the initial velocity from the final velocity, then divide the result by the time interval. The final result is your average acceleration over that time.
resultant acceleration formula|acceleration calculator
PH0 · which formula is used to calculate acceleration
PH1 · how to find resultant acceleration
PH2 · formula for velocity using acceleration
PH3 · force mass acceleration calculator
PH4 · examples of acceleration problems
PH5 · equation to solve for acceleration
PH6 · acceleration practice problems with answers
PH7 · acceleration calculator
PH8 · Iba pa